Task
两种类型Task
ResultTask和ShuffleMapTask
由不同Stage产生,如果是Shuffle Stage就是后者,否则产生ResultTask
1. ResultTask
A task that sends back the output to the driver application.
ResultTask.scala
override def runTask(context: TaskContext): U = {
// Deserialize the RDD and the func using the broadcast variables.
val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance()
val (rdd, func) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[T], (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U)](
ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
metrics = Some(context.taskMetrics)
func(context, rdd.iterator(partition, context))
}
}
注意runTask返回值
2. ShuffleMapTask
Divides the elements of an RDD into multiple buckets (based on a partitioner specified in the ShuffleDependency).
Where we are
执行的代码对应Sample里是
words.map(word => (word, 1))
Do what
把这个stage的计算结果写到硬盘上,所以内存计算的cache和recompute只是在这个stage内
override def runTask(context: TaskContext): MapStatus = {
// Deserialize the RDD using the broadcast variable.
val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance()
val (rdd, dep) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _])](
ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
var writer: ShuffleWriter[Any, Any] = null
try {
val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager
writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](dep.shuffleHandle, partitionId, context)
//根据不同的shuffleHandler得到不同的ShuffleWriter,不同的写出数据
writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]])
return writer.stop(success = true).get
}
}
ShuffleMapTask的所做的工作就是把这个task的partition的数据依据shuffleHandle写出 writer有两种HashShuffleWriter和SorterShuffleWriter,1.2中缺省是SotShuffleWriter
SortShuffle
SortShuffleWriter
override def write(records: Iterator[_ <: Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
if (!dep.aggregator.isDefined) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Aggregator is empty for map-side combine")
}
//缺省把这个partition里的数据combine,如果内存不够可能写临时文件
//然后按partitioner的定义里的值写到数据文件里,具体看ExternalSorter
sorter = new ExternalSorter[K, V, C](
dep.aggregator, Some(dep.partitioner), dep.keyOrdering, dep.serializer)
sorter.insertAll(records)
} else {
sorter = new ExternalSorter[K, V, V](
None, Some(dep.partitioner), None, dep.serializer)
sorter.insertAll(records)
}
//mapId就是partitionId,和shuffleId构成了一个文件
val outputFile = shuffleBlockManager.getDataFile(dep.shuffleId, mapId)
val blockId = shuffleBlockManager.consolidateId(dep.shuffleId, mapId)
logInfo(s"hxm: blockId: $blockId, outputFile: $outputFile")
//ExternalSorter会groupByPartition生成按reduceId 分片的数据
val partitionLengths = sorter.writePartitionedFile(blockId, context, outputFile)
//把每个partition的数据长度信息写到.index文件
shuffleBlockManager.writeIndexFile(dep.shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths)
//形成状态文件后面MapoutputTracker用到,mapStatus会传到dagScheduler里,参见DAGScheduler里task result handle的ShuffleMapTask部分,表示map完成了
mapStatus = MapStatus(blockManager.shuffleServerId, partitionLengths)
}
Executor 0
16/02/23 14:40:24 INFO SortShuffleWriter: hxm: blockId: shuffle_0_0_0, outputFile: /tmp/spark-local-20160223144023-c827/0c/shuffle_0_0_0.data
Executor 1
16/02/23 14:40:24 INFO SortShuffleWriter: hxm: blockId: shuffle_0_1_0, outputFile: /tmp/spark-local-20160223144023-3867/15/shuffle_0_1_0.data
ExternalSorter
def writePartitionedFile(
blockId: BlockId,
context: TaskContext,
outputFile: File): Array[Long] = {
//partitionIterator会将数据按reduceId做合并,形成按分区
for ((id, elements) <- this.partitionedIterator) {
if (elements.hasNext) {
//写到文件里?不能用内存么? 为什么不能用Tachyon?
val writer = blockManager.getDiskWriter(
blockId, outputFile, ser, fileBufferSize, context.taskMetrics.shuffleWriteMetrics.get)
for (elem <- elements) {
writer.write(elem)
}
writer.commitAndClose()
val segment = writer.fileSegment()
//得到每个partition内写了多少数据到数据文件里
lengths(id) = segment.length
}
}
}
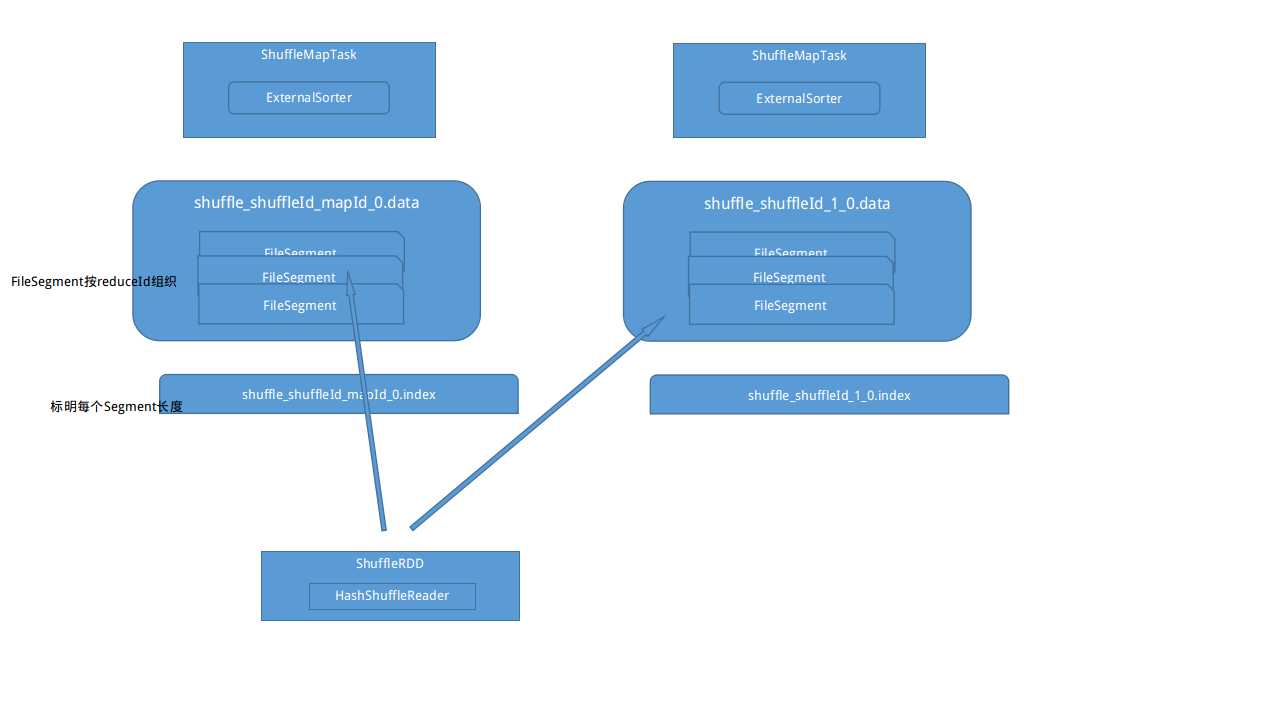
HashShuffle
如果是HashShuffle则
override def write(records: Iterator[_ <: Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
val iter = if (dep.aggregator.isDefined) {
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
dep.aggregator.get.combineValuesByKey(records, context)
} else {
records
}
} else if (dep.aggregator.isEmpty && dep.mapSideCombine) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Aggregator is empty for map-side combine")
} else {
records
}
for (elem <- iter) {
//对应的是按key写出
val bucketId = dep.partitioner.getPartition(elem._1)
shuffle.writers(bucketId).write(elem)
}
}
比如示例代码里是“hello 1","hello 1"两条记录写到同一个地方
3. Task result handle
在Executor里的TaskRunner中获得结果 Executor.scala
class TaskRunner(
execBackend: ExecutorBackend, val taskId: Long, taskName: String, serializedTask: ByteBuffer)
extends Runnable {
override def run() {
logInfo(s"Running $taskName (TID $taskId)")
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.RUNNING, EMPTY_BYTE_BUFFER)
try {
val (taskFiles, taskJars, taskBytes) = Task.deserializeWithDependencies(serializedTask)
task = ser.deserialize[Task[Any]](taskBytes, Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
// Run the actual task and measure its runtime.
taskStart = System.currentTimeMillis()
val value = task.run(taskId.toInt)
val taskFinish = System.currentTimeMillis()
val resultSer = SparkEnv.get.serializer.newInstance()
val beforeSerialization = System.currentTimeMillis()
//序列化task结果
val valueBytes = resultSer.serialize(value)
val afterSerialization = System.currentTimeMillis()
val directResult = new DirectTaskResult(valueBytes, accumUpdates, task.metrics.orNull)
val serializedDirectResult = ser.serialize(directResult)
val resultSize = serializedDirectResult.limit
// directSend = sending directly back to the driver
val serializedResult = {
//各种结果方式
...
logInfo(s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). $resultSize bytes result sent to driver")
serializedDirectResult
}
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FINISHED, serializedResult)
}
}
}
override def run() {
val value = task.run(taskId.toInt)
val valueBytes = resultSer.serialize(value)
val directResult = new DirectTaskResult(valueBytes, accumUpdates, task.metrics.orNull)
// directSend = sending directly back to the driver
val serializedDirectResult = ser.serialize(directResult)
val serializedResult = {
...
}
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FINISHED, serializedResult)
16/02/15 16:20:31 INFO Executor: Running task 0.0 in stage 0.0 (TID 0)
16/02/15 16:20:32 INFO Executor: Finished task 0.0 in stage 0.0 (TID 0). 1899 bytes result sent to driver
backend送结果到driver CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend.scala
override def statusUpdate(taskId: Long, state: TaskState, data: ByteBuffer) {
driver ! StatusUpdate(executorId, taskId, state, data)
}
在app端收到结果 CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.scala
class DriverActor(sparkProperties: Seq[(String, String)]) extends Actor with ActorLogReceive {
def receiveWithLogging = {
case StatusUpdate(executorId, taskId, state, data) =>
scheduler.statusUpdate(taskId, state, data.value)
...
TaskSchedulerImpl.scala
if (state == TaskState.FINISHED) {
taskSet.removeRunningTask(tid)
taskResultGetter.enqueueSuccessfulTask(taskSet, tid, serializedData)
}
def handleSuccessfulTask(
taskSetManager: TaskSetManager,
tid: Long,
taskResult: DirectTaskResult[_]) = synchronized {
taskSetManager.handleSuccessfulTask(tid, taskResult)
}
16/02/15 14:28:27 INFO TaskSetManager: Finished task 0.0 in stage 1.0 (TID 2) in 544 ms on 192.168.101.32 (2/2)
最后调用dagScheduler.taskEnded()
def taskEnded(
task: Task[_],
reason: TaskEndReason,
result: Any,
accumUpdates: Map[Long, Any],
taskInfo: TaskInfo,
taskMetrics: TaskMetrics) {
eventProcessActor ! CompletionEvent(task, reason, result, accumUpdates, taskInfo, taskMetrics)
}
case completion @ CompletionEvent(task, reason, _, _, taskInfo, taskMetrics) =>
dagScheduler.handleTaskCompletion(completion)
private[scheduler] def handleTaskCompletion(event: CompletionEvent) {
event.reason match {
case Success =>
stage.pendingTasks -= task
task match {
case rt: ResultTask[_, _] =>
stage.resultOfJob match {
case Some(job) =>
if (!job.finished(rt.outputId)) {
job.finished(rt.outputId) = true
job.numFinished += 1
// If the whole job has finished, remove it
if (job.numFinished == job.numPartitions) {
//输出log
markStageAsFinished(stage)
}
}
}
16/02/15 14:28:27 INFO DAGScheduler: Stage 1 (saveAsTextFile at WordCount.scala:25) finished in 0.543 s
结果处理
TaskRunner.run()
val directResult = new DirectTaskResult(valueBytes, accumUpdates, task.metrics.orNull)
val serializedDirectResult = ser.serialize(directResult)
val resultSize = serializedDirectResult.limit
// directSend = sending directly back to the driver
val serializedResult = {
//缺省maxResultSize 1G, dropping it???
if (maxResultSize > 0 && resultSize > maxResultSize) {
logWarning(s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). Result is larger than maxResultSize " +
s"(${Utils.bytesToString(resultSize)} > ${Utils.bytesToString(maxResultSize)}), " +
s"dropping it.")
ser.serialize(new IndirectTaskResult[Any](TaskResultBlockId(taskId), resultSize))
} else if (resultSize >= akkaFrameSize - AkkaUtils.reservedSizeBytes) {
//如果大于frameSize在放到blockManager里
val blockId = TaskResultBlockId(taskId)
env.blockManager.putBytes(
blockId, serializedDirectResult, StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER)
logInfo(
s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). $resultSize bytes result sent via BlockManager)")
ser.serialize(new IndirectTaskResult[Any](blockId, resultSize))
} else {
logInfo(s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). $resultSize bytes result sent to driver")
serializedDirectResult
}
}
4. Error handling
TaskRunner catch task.run()的exception,然后更新backend的状态
catch {
case ffe: FetchFailedException => {
val reason = ffe.toTaskEndReason
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FAILED, ser.serialize(reason))
}
case _: TaskKilledException | _: InterruptedException if task.killed => {
logInfo(s"Executor killed $taskName (TID $taskId)")
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.KILLED, ser.serialize(TaskKilled))
}
case t: Throwable => {
// Attempt to exit cleanly by informing the driver of our failure.
// If anything goes wrong (or this was a fatal exception), we will delegate to
// the default uncaught exception handler, which will terminate the Executor.
logError(s"Exception in $taskName (TID $taskId)", t)
//包装成ExceptionFailure
val reason = new ExceptionFailure(t, metrics)
//更新backend状态,然后backend发消息到driver(schedulerBackend里的driverActor)更新状态 driver又更新scheduler里的状态
//设置状态是FAILED
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FAILED, ser.serialize(reason))
// Don't forcibly exit unless the exception was inherently fatal, to avoid
// stopping other tasks unnecessarily.
if (Utils.isFatalError(t)) {
SparkUncaughtExceptionHandler.uncaughtException(t)
}
}
}
TaskScheduler
def statusUpdate(tid: Long, state: TaskState, serializedData: ByteBuffer) {
//状态是FAILED, KILLED, LOST
if (Set(TaskState.FAILED, TaskState.KILLED, TaskState.LOST).contains(state)) {
taskSet.removeRunningTask(tid)
taskResultGetter.enqueueFailedTask(taskSet, tid, state, serializedData)
}
}
TaskResultGetter
def enqueueFailedTask(taskSetManager: TaskSetManager, tid: Long, taskState: TaskState,
serializedData: ByteBuffer) {
var reason : TaskEndReason = UnknownReason
//放在另外的线程里执行,估计是因为这是在statusUpdate里调的,而statusUpdate在driverActor的消息处理里
getTaskResultExecutor.execute(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.logUncaughtExceptions {
if (serializedData != null && serializedData.limit() > 0) {
reason = serializer.get().deserialize[TaskEndReason](
serializedData, Utils.getSparkClassLoader)
}
//这里调taskSetManager.handleFailedTask
scheduler.handleFailedTask(taskSetManager, tid, taskState, reason)
}
})
}
TaskSetManager.scala
/**
* Marks the task as failed, re-adds it to the list of pending tasks, and notifies the
* DAG Scheduler.
*/
def handleFailedTask(tid: Long, state: TaskState, reason: TaskEndReason) {
val info = taskInfos(tid)
removeRunningTask(tid)
info.markFailed()
var taskMetrics : TaskMetrics = null
val failureReason = s"Lost task ${info.id} in stage ${taskSet.id} (TID $tid, ${info.host}): " +
reason.asInstanceOf[TaskFailedReason].toErrorString
reason match {
//FetchFailed 认为已经成功?设成zombie?
case fetchFailed: FetchFailed =>
logWarning(failureReason)
if (!successful(index)) {
successful(index) = true
tasksSuccessful += 1
}
// Not adding to failed executors for FetchFailed.
isZombie = true
//前面的包装的Throwable
case ef: ExceptionFailure =>
taskMetrics = ef.metrics.orNull
//序列化的问题
if (ef.className == classOf[NotSerializableException].getName) {
// If the task result wasn't serializable, there's no point in trying to re-execute it.
logError("Task %s in stage %s (TID %d) had a not serializable result: %s; not retrying"
.format(info.id, taskSet.id, tid, ef.description))
abort("Task %s in stage %s (TID %d) had a not serializable result: %s".format(
info.id, taskSet.id, tid, ef.description))
return
}
val key = ef.description
val now = clock.getTime()
val (printFull, dupCount) = {
if (recentExceptions.contains(key)) {
val (dupCount, printTime) = recentExceptions(key)
if (now - printTime > EXCEPTION_PRINT_INTERVAL) {
recentExceptions(key) = (0, now)
(true, 0)
} else {
recentExceptions(key) = (dupCount + 1, printTime)
(false, dupCount + 1)
}
} else {
recentExceptions(key) = (0, now)
(true, 0)
}
}
if (printFull) {
logWarning(failureReason)
} else {
logInfo(
s"Lost task ${info.id} in stage ${taskSet.id} (TID $tid) on executor ${info.host}: " +
s"${ef.className} (${ef.description}) [duplicate $dupCount]")
}
case e: TaskFailedReason => // TaskResultLost, TaskKilled, and others
logWarning(failureReason)
case e: TaskEndReason =>
logError("Unknown TaskEndReason: " + e)
}
// always add to failed executors
failedExecutors.getOrElseUpdate(index, new HashMap[String, Long]()).
put(info.executorId, clock.getTime())
//对于ExceptionFailure scheduler不做啥
sched.dagScheduler.taskEnded(tasks(index), reason, null, null, info, taskMetrics)
//task重新加到taskSetManager里等着重新执行
addPendingTask(index)
if (!isZombie && state != TaskState.KILLED) {
assert (null != failureReason)
numFailures(index) += 1
//如果大于最大失败则退出,由spark.task.maxFailures决定,缺省4,local的话是1
if (numFailures(index) >= maxTaskFailures) {
logError("Task %d in stage %s failed %d times; aborting job".format(
index, taskSet.id, maxTaskFailures))
//标志task zombie=true, 向dagScheduler发消息TaskSetFailed,后者abortStage
abort("Task %d in stage %s failed %d times, most recent failure: %s\nDriver stacktrace:"
.format(index, taskSet.id, maxTaskFailures, failureReason))
return
}
}
//zombie或结束
maybeFinishTaskSet()
}
5. Kill a task
dagScheduler调用taskScheduler.cancelTask() scheduler可以通过driverActor发出KillTask消息,driver又发到executor 杀一个任务通过设置taskThread interrrupt()来杀执行线程,然后taskRunner抛出TaskKilledException 通知executorBackend,再想driver发出StatusUpdate消息,接下来类似上面Error handling
catch {
case _: TaskKilledException | _: InterruptedException if task.killed => {
logInfo(s"Executor killed $taskName (TID $taskId)")
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.KILLED, ser.serialize(TaskKilled))
}